What Are Adjuvants?
In simple terms, adjuvants are substances that assist or enhance the body’s immune response. In immunology, an adjuvant is defined as any substance that accelerates, prolongs, or amplifies an antigen-specific immune response when combined with a vaccine antigen. Adjuvants play a critical role in increasing the efficacy of vaccines and immunotherapies.
Types of Adjuvants
1. Mineral Salt Adjuvants
These adjuvants primarily include aluminum and calcium-based compounds that promote immune responses by forming a depot at the site of injection.
Examples include:
- Aluminium phosphate
- Calcium phosphate
- Magnesium hydroxide
2. Oil-in-Water Emulsions
These consist of squalene-based oil emulsified in water, with the antigen dispersed in the aqueous phase. They are known to stimulate strong immune responses.
Examples include:
- Freund’s adjuvant
- MF59
- AS03
3. Saponin-Based Adjuvants
Saponins stimulate the release of cytokines and chemokines, regulate immune cell recruitment, and facilitate intracellular signaling. Due to their ability to activate the immune system, they are used as adjuvants.
Examples include:
- Quil A (derived from Quillaja saponaria)
- Iscomatrix
4. Polysaccharide and Liposome Adjuvants
Polysaccharide adjuvants such as dextran, chitin, and chitosan enhance the immune response through various pathways. Liposome-based adjuvants like virosomes and cationic lipids (e.g., DOTAP) aid in antigen delivery and presentation.
5. Cytokine Adjuvants
Certain cytokines function as adjuvants by boosting immune responses against viral, bacterial, or parasitic vaccines.
Examples include:
- Interleukin-2 (IL-2)
- Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ)
- Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
6. Other Adjuvants
Bacterial derivative adjuvants include lipopolysaccharides (LPS), muramyl dipeptide (MDP), and outer membrane vesicles (OMVs).
Synthetic adjuvants include polyethyleneimine, poly-L-lysine, and polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA).
Natural adjuvants include beta-glucans derived from yeast or mushrooms and plant-based saponins.
Mechanisms of Action of Adjuvants
1. Depot Formation
This involves the slow release of antigen at the injection site, ensuring prolonged exposure to immune cells.
Examples: Aluminum salts, oil-in-water emulsions
2. Immunopotentiation
Adjuvants enhance antigen presentation by activating immune cells such as dendritic cells and T-cells.
Examples: Quil A, QS-21, liposomes
3. Immunostimulation
They activate pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which in turn induce cytokine production, especially Th1 and Th2 responses.
Examples: CpG motifs, LPS, MDP
4. Antigen Delivery
Adjuvants improve the uptake and processing of antigens by targeting specific immune cells or tissues.
Examples: Liposomes, nanoparticles, virosomes
5. Immune Cell Activation
They promote dendritic cell maturation, T-cell activation and proliferation, B-cell activation, and antibody production.
Examples: Cytokines, immunostimulatory sequences
6. Modulation of Immune Response
Adjuvants can balance Th1/Th2 responses and, in some cases, induce immune tolerance or suppression.
Examples: Glucocorticoids, immunosuppressive cytokines
Applications of Adjuvants
In Vaccines
Adjuvants are used in several vaccines to enhance immune responses:
- Influenza vaccines: Fluad, Fluzone
- HPV vaccines: Cervarix, Gardasil
- Hepatitis B vaccine: Recombivax
- Pneumococcal vaccines: Prevnar 13
- Meningococcal vaccines: Menactra
In Immunotherapy
- Cancer treatment (e.g., checkpoint inhibitors)
- Allergy desensitization therapy
- Treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis
In Diagnostics
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
- Western blotting
- Immunohistochemistry
- Flow cytometry
In Research
- Immunology research
- Vaccine development
- Cancer biology
- Infectious disease studies
In Cosmetic and Dermatology
- Skin immunotherapy
- Hair loss treatments
- Anti-aging therapies
Other Applications
- Treatment of food and environmental allergies
- Asthma therapy
- Immunomodulatory treatments for cancer (e.g., IL-2, IFN-γ)
- Gene therapy and adoptive T-cell therapy
Haptens
What Are Haptens?
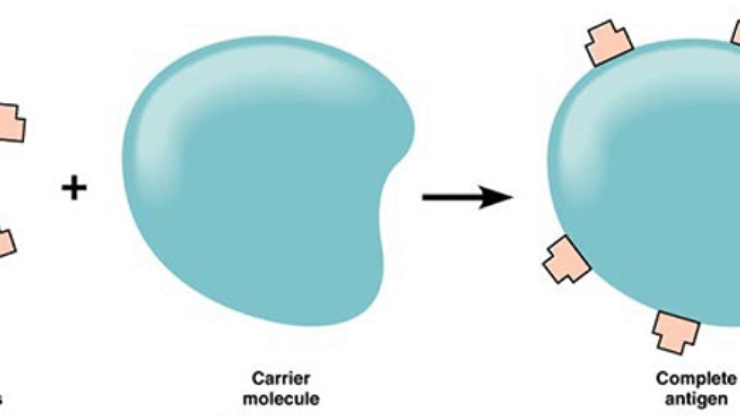
The term hapten is derived from the Greek word haptein, meaning “to fasten.” Coined by Karl Landsteiner, haptens are small, non-biological molecules that bind to immune receptors but are unable to trigger an immune response on their own. They are considered incomplete antigens, as they require attachment to a carrier molecule to become immunogenic.
Characteristics of Haptens
Physical Characteristics
- Typically small in size (less than 1000 Dalton)
- Simple molecular structure
- Can be hydrophilic or hydrophobic
Immunological Characteristics
- Non-immunogenic alone
- Become immunogenic when conjugated with carrier proteins
- Can bind to antibodies or T-cell receptors
Chemical Characteristics
- React with functional groups such as -NH₂ and -SH
- Form covalent bonds with carriers
- Stable in aqueous solutions and soluble in organic solvents
Biological Characteristics
- Can trigger autoimmune or allergic responses when bound to carriers
- Interact with biological molecules like proteins and immune cells
- Offer metabolic stability in biological systems
Types of Haptens
1. Based on Reactivity
- Electrophilic haptens: Dinitrophenol
- Nucleophilic haptens: Sulfonamides
- Radical-forming haptens: Heavy metals
2. Based on Origin
- Natural haptens: Urushiol (from poison ivy), animal venom
- Synthetic haptens: Drugs and pesticides
- Semi-synthetic haptens: Modified natural compounds
3. Based on Structure
- Simple haptens: Univalent; do not precipitate with antibodies
- Complex haptens: Polyvalent; capable of forming antigen-antibody complexes
4. Other Categories
Small molecule haptens:
- Drugs: Penicillin, sulfonamides
- Toxins and pesticides: DDT, diphtheria toxin
- Pollutants: Heavy metals
Peptide haptens:
- Short synthetic peptides
- Tumor-associated peptides
Carbohydrate haptens:
- Sugars: Glucose, galactose
- Glycoproteins and polysaccharides
Lipid haptens:
- Phospholipids, glycolipids, steroids
Nucleic acid haptens:
- DNA, RNA, oligonucleotides
Synthetic haptens:
- DNP (Dinitrophenol), FITC (Fluorescein isothiocyanate)
Hormonal haptens:
- Steroid hormones: Estrogen, testosterone
- Peptide hormones: Insulin
Importance of Haptens
In Immunology
- Aid in the design of conjugate vaccines
- Help understand immune mechanisms and allergic reactions
In Medicine
- Used in diagnostic tools like ELISA and Western blotting
- Assist in therapeutic development and disease understanding
In Pharmacology and Toxicology
- Support drug design and targeted delivery
- Enable evaluation of drug metabolism and toxicity
- Aid in environmental risk assessments
In Cancer Research
- Help identify cancer-specific antigens
- Assist in developing cancer vaccines and precision therapies
In Environmental Science and Biotechnology
- Detect environmental pollutants such as heavy metals
- Facilitate ecological toxicity assessments and bioremediation
- Enable protein engineering and biosensor development