1. The Saltwater Crocodile: A Force of Nature

Bite Force
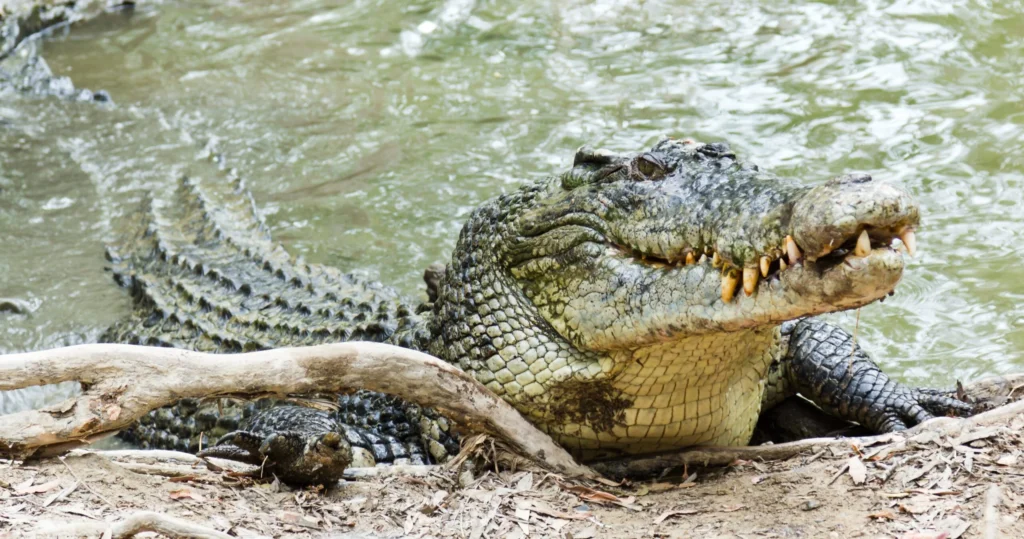
Scientific evidence recently revealed that the saltwater crocodile, also known as Crocodylus porosus, has the strongest bite force among living animals—recorded at over 3,700 pounds per square inch. This extreme force comes from highly specialized jaw muscles that evolved to maximize downward power.
Massive Jaw Muscle Strength
Saltwater crocodiles have jaw-closing muscles that are about 50% more powerful than those of large predators like lions. These muscles are adapted for explosive strength, allowing the crocodile to deliver fatal bites quickly.
Body Teeth
Their conical teeth interlock tightly when the jaws close, delivering a grip that’s nearly impossible to break. These teeth are not designed for slicing but for holding and controlling prey. Their enamel resists wear, so sharpness is retained over time.
2. The Nile Crocodile: A Close Second
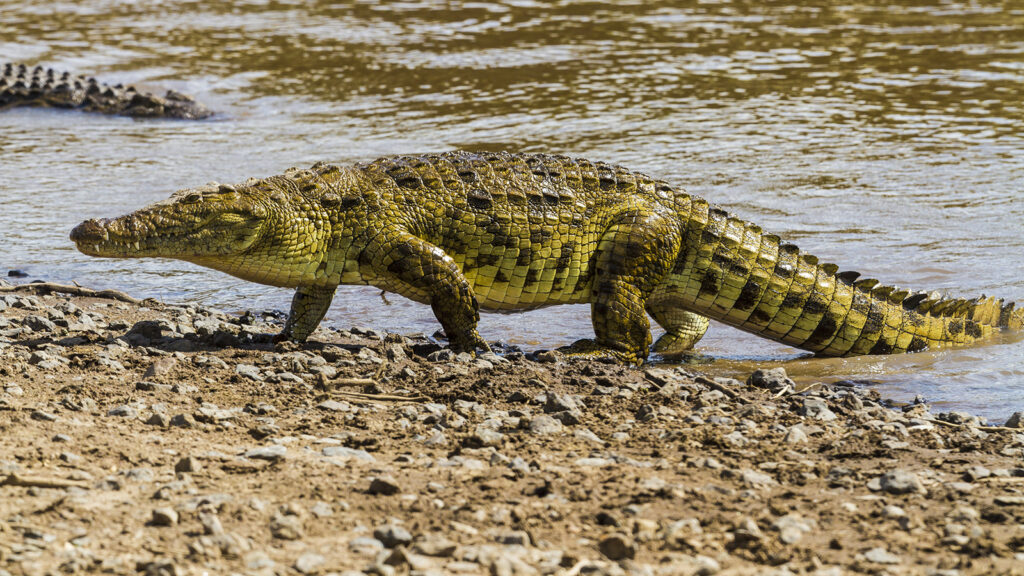

Bite Force Variability
The Nile crocodile’s bite force varies but can exceed 3,000 PSI, depending on factors like age, size, and health. Larger individuals—especially those over 15 feet—have proportionately stronger bites due to muscle and skeletal scaling.
Hunting Strategy
Usually solitary, Nile crocodiles can exhibit cooperative hunting during the dry season. When water levels drop, they collaborate to trap larger prey like zebras and wildebeests, a rare behavior in reptiles.
Tooth Replacement
Like all crocodilians, Nile crocodiles are polyphyodonts, meaning they continuously replace their teeth. This evolutionary trait ensures they always have sharp, functional teeth—an adaptation traced back 200 million years.
3. The Great White Shark: A Bite to Remember
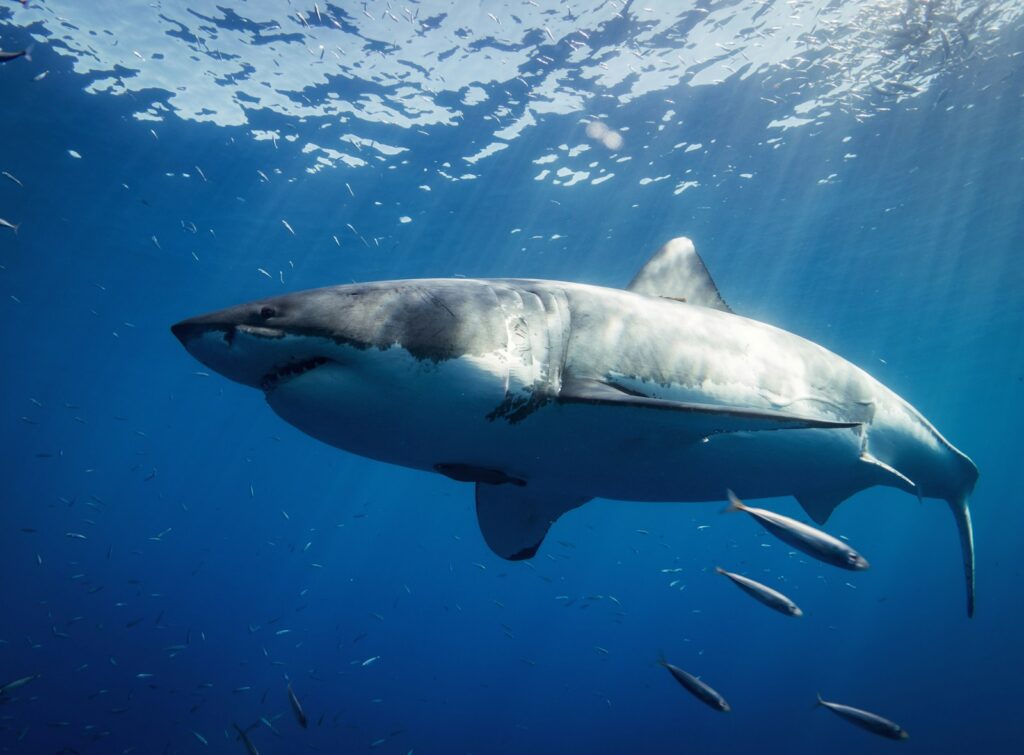

Approximation of Bite Force
A large great white shark is estimated to have a bite force exceeding 4,000 PSI. This power stems from strong jaw muscles and a unique cranial structure that lets the upper jaw extend forward during a bite for a better grip.
Replacement of Teeth
Great white sharks constantly regenerate rows of serrated teeth. When one is lost, another from behind takes its place—ensuring the shark is always ready to tear through flesh.
Sensory Capabilities
Their ampullae of Lorenzini detect the faintest electrical signals from prey, while their exceptional sense of smell allows them to locate targets from miles away—even in murky water.
4. The Hippopotamus: An Unlikely Challenger
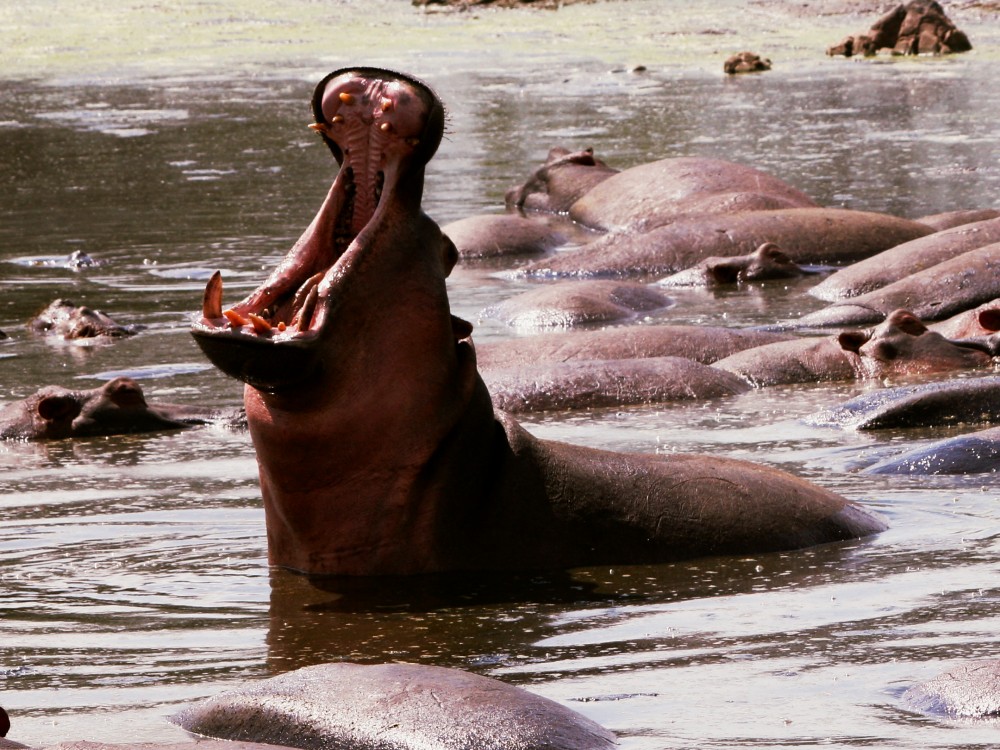

Variability of Bite Force
Hippopotamus amphibius can exert a bite force of over 1,800 PSI. This force is primarily used in defense and territorial disputes. Aggression levels and emotional states influence the strength of their bite.
Jaw Muscle Strength
Hippos have some of the strongest jaw muscles in the animal kingdom. Their large skulls support these muscles, allowing them to chew tough vegetation and crush bones when necessary.
Aggression Towards Territory
Hippos are among the deadliest animals in Africa, responsible for more human deaths than any other large mammal. Their aggression, combined with a powerful bite, makes them especially dangerous when provoked.
5. The Jaguar: A Stealthy Predator
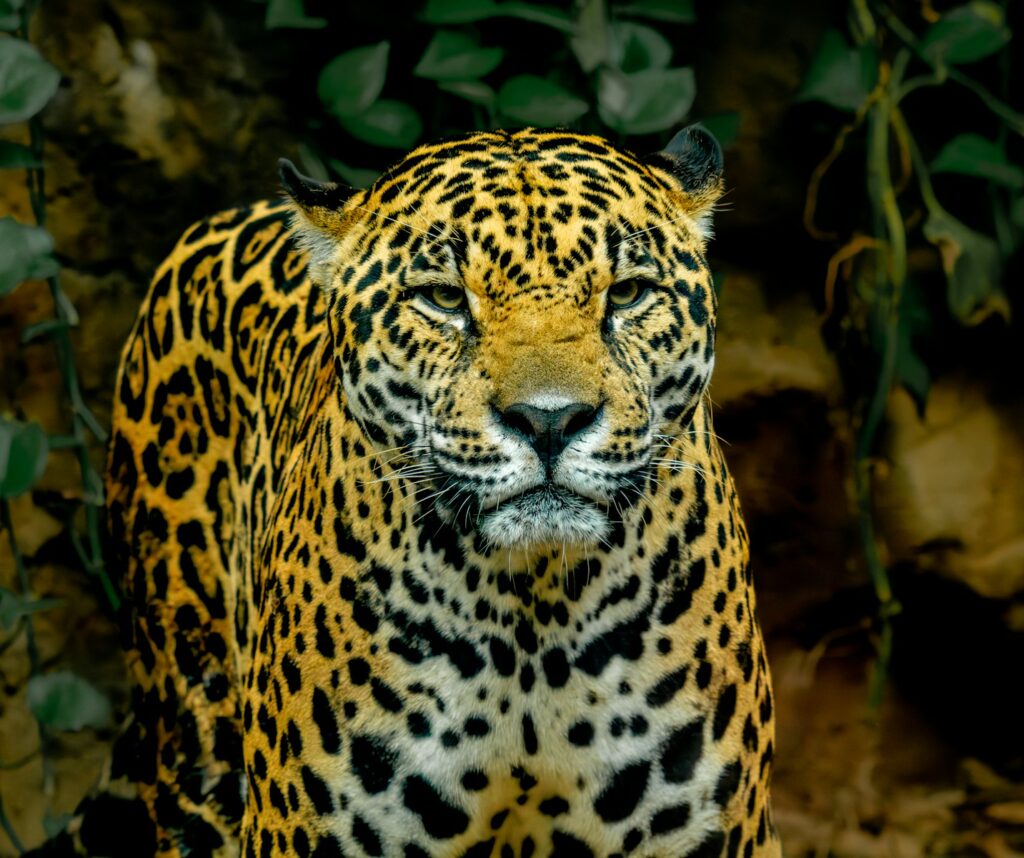

Variation in Bite Force
The jaguar (Panthera onca) has the strongest bite of any big cat—over 1,500 PSI. This force is powerful enough to crack turtle shells, which are a common part of their diet.
Hunting Strategy
Unlike other big cats that go for the throat, jaguars often target the skull. Their precise bite crushes the temporal bones, instantly fatally injuring the prey.
Bite Strength Adaptation
Jaguars have a stocky build and thick, short teeth, which are ideal for crushing rather than slicing. This anatomy amplifies their ability to deliver targeted, high-pressure bites.
6. The Komodo Dragon: Nature’s Venomous Giant
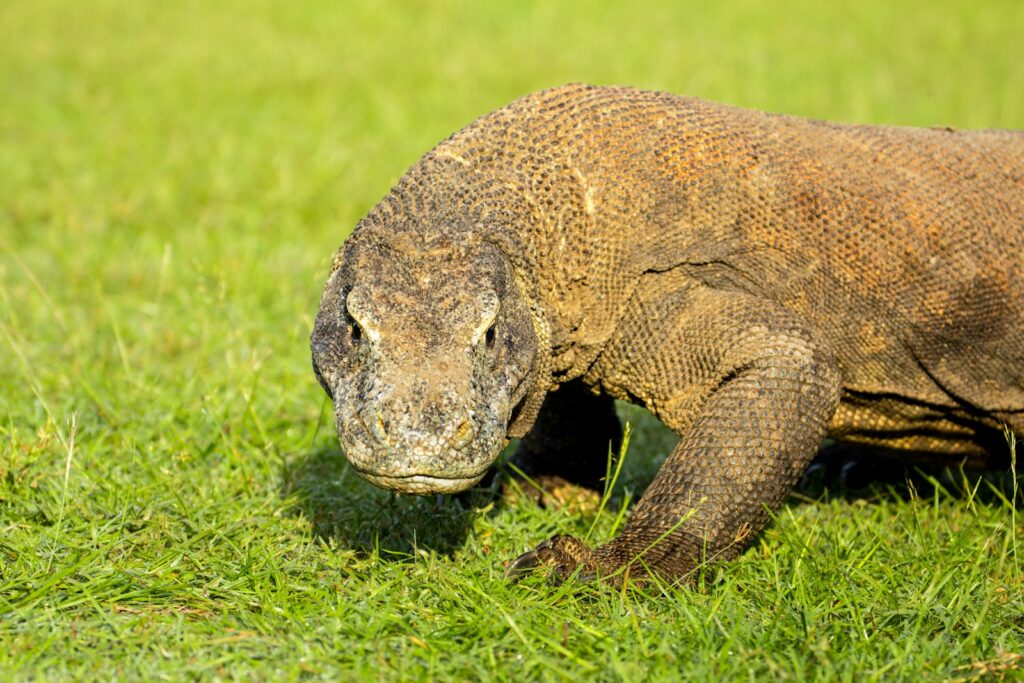

Venomous Saliva
Recent studies show that Komodo dragons have venom glands that secrete toxins. These toxins cause blood loss, low blood pressure, and shock—leading to faster death in prey.
Hunting Strategy
Komodo dragons ambush their prey with short, explosive sprints. After delivering a venomous bite, they track the weakened animal for hours—or even days—until it collapses.
Regenerative Abilities
They also possess strong regenerative capabilities, quickly healing from injuries. Their robust immune systems help them survive infections that could kill other animals.
Conclusion
Animal bite force is a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation. From the explosive jaws of the saltwater crocodile to the venom-laced bite of the Komodo dragon, each species has evolved unique strategies for survival. These powerful adaptations reveal nature’s creativity and specialization at its finest.